Why install solar panels on a boat ?
The energy consumption on board of boats is increasing due to comfort equipment and electronics. It is common on a sailboat to have to use the diesel engine for some hours a day just to recharge the batteries. This is bad for the motor that runs without charge and at low revs and for the batteries that never get to be fully charged and have ridiculously low efficiency.
Technological advances concerning solar panels make them almost essential on a boat nowadays. We use them to keep the batteries charged when the boat is not being used and thus avoid having to connect to the quay (which is more and more often forbidden by harbor authorities due to the risk of fire) or to spread the consumption which is ever more important on board.
They are the ideal complement to hydro generation for electrically powered boats.

Choosing your solar panels
The first obvious point to validate is the “marinization” of the material. In the sea, the material is exposed to strong forces: salt, water, wind and sun… You have to choose a manufacturer that uses appropriate materials and who has a long experience in the field.
The cells
There are 3 types of cells: amorphous, polycrystalline and monocrystalline
- Amorphes cells have practically disappeared from the market because they have a low efficiency*
- Polycrystalline cells are made with silica shards that are amalgamated. The efficiency is around 14% and they age poorly
- Monocrystalline cells are made from pure silica bars. They have an efficiency between 17% and 20%. They are, however, more expensive.
Back Contact technology allows the cells to be connected from their rear part, which optimizes the surface exposed to the sun and therefore increases the efficiency. It is thus possible to achieve an efficiency of 25%.
Since space is limited on a boat, it is better to choose monocrystalline solar panels with Back Contact technology. The difference in price when bought will be amortized by its higher production.
*Efficiency= Ratio between electricity actually produced and the light energy captured.
Flexible or rigid ?
Solar panels are traditionally rigid and are often placed on the davit of the boat. This is the most efficient solution because they are well ventilated and can even be oriented, however they are heavy and take a lot of space. You can therefore not install a lot of them.
Nowadays there are flexible solar panels that can be used on a slightly curved surface (roof, bimini etc) and some of them even allow you to walk on them (you should however avoid installing them on places where there is intensive passage).
These panels use the same cells as rigid solar panels which are coated with a special resin which could also act as an anti-slip and there is a lot of choice. But a good price does not always mean durability. The marine world is particularly demanding, you should choose high quality and manufacturers who have a lot of experience in the marine world.
Flexible panels are very light and can be installed more easily on the boat. Some modern monohulls can withstand more than 3 kW of solar panels.
The main disadvantage of the flexible panel is that it has to be installed flat on the deck and it might not always be oriented towards the sun, besides connecting them in series could be problematic if one of the panels connected in series is under the shadow.
A good solution might be foldable and removable panels which you can position according to the sun when you are at anchor.
Choosing the right regulator
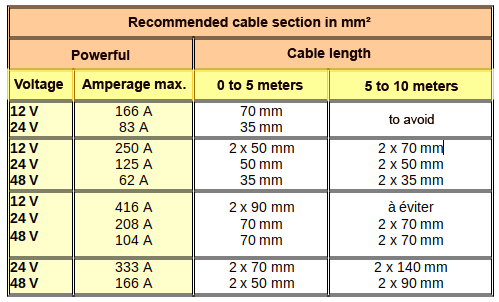
Once the right panels have been chosen, it is time to think about the rest of the installation, which will also determine the efficiency of the entire production chain. The section of the cables depending on the power transmitted (ohm law) and the distance from the batteries, the quality of the connectors and connections and finally the regulator.
It would be a shame to lose 20% of efficiency to save a few euros.
The regulator transforms the voltage output of the panels into a battery charging voltage. It is therefore necessary first of all to make sure that it is compatible with its battery pack (Lithium, AGM which do not have the same load curves)
There are 2 types of regulators : PWM and MPPT
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking), the former are inexpensive and simply lower the voltage at the output of the panels to 14 V for the batteries without modifying the amperage. If the panel output is 20 volts then the regulator will lower it to 14 V to charge the battery and we therefore lose 30% since the amperage remains the same.
- MPPTs continuously adjust the amperage to the voltage output from the panels, the best MPPTs achieve efficiencies above 95%.

What can we expect from the production of solar panels ?
Depending on the region, the position and the quality of the solar panels, we can expect a daily production of 3 to 5 times the initial power (Wp *) of the panel. For a 100 Wp panel, we will therefore get a production between 300 WH and 450 WH.
*Wp: The watt-peak is the maximum power of a device. Its unit is the watt. For a photovoltaic installation, this is the maximum electrical power that can be produced by the cells under standard conditions of light, position and temperature.
If the temperature exceeds 25 ° C, it is necessary to count a reduction in its performance of 0,4% per additional degree.
Note: Ohm’s Law implies that the heat dissipation due to the resistance of a cable are Pc (Watt) = Rc x I², where Rc is the resistance of the cable. This formula shows that for a given cable dissipation, the effective section of the cable can be reduced by a factor of 4 by doubling the voltage.
Importance of good connections
80% of functional failures on board are due to bad connections!
In addition to those resulting from improper tightening of the battery terminals, many electrical disorders are due to terminals that are not suitable or which are not making enough contact with the cables.
The good advice is therefore not only to take care to avoid this type of mistake, but above all to weld all the electrical tin wires to the terminals.
Finally, the terminals must be protected from any unwanted contact with metallic objects or parts of the boat, which could cause an electrical leak or a short circuit.
Which brand of solar panel should you buy ?
We have chosen 2 of the leaders in the field of photovoltaics
- VICTRON for solid solar panels
- SUNBEAM for flexible panels
VICTRON Energy
Victron Energy is a Dutch company specialized in renewable energy with a worldwide presence and a leader in its field. It is known for its innovative solutions and the reliability of its products, which have a warranty of 5 years. It has a marine section dedicated to the nautical world
SUNBEAM
SUNBEAM is a Swedish company recognized for its innovative solutions for the production of photovoltaic energy.
Specialized in flexible solar panels for boats, it offers a wide range of flexible or foldable solar panels.
- The most efficient cells on the market (monocrystalline, back contact technology) offering 25% efficiency
- Revolutionary coating which has a non-slip effect
- Shadow Optimized technology for better efficiency when in shadow
- Anti UV treatment
- 5 year warranty

